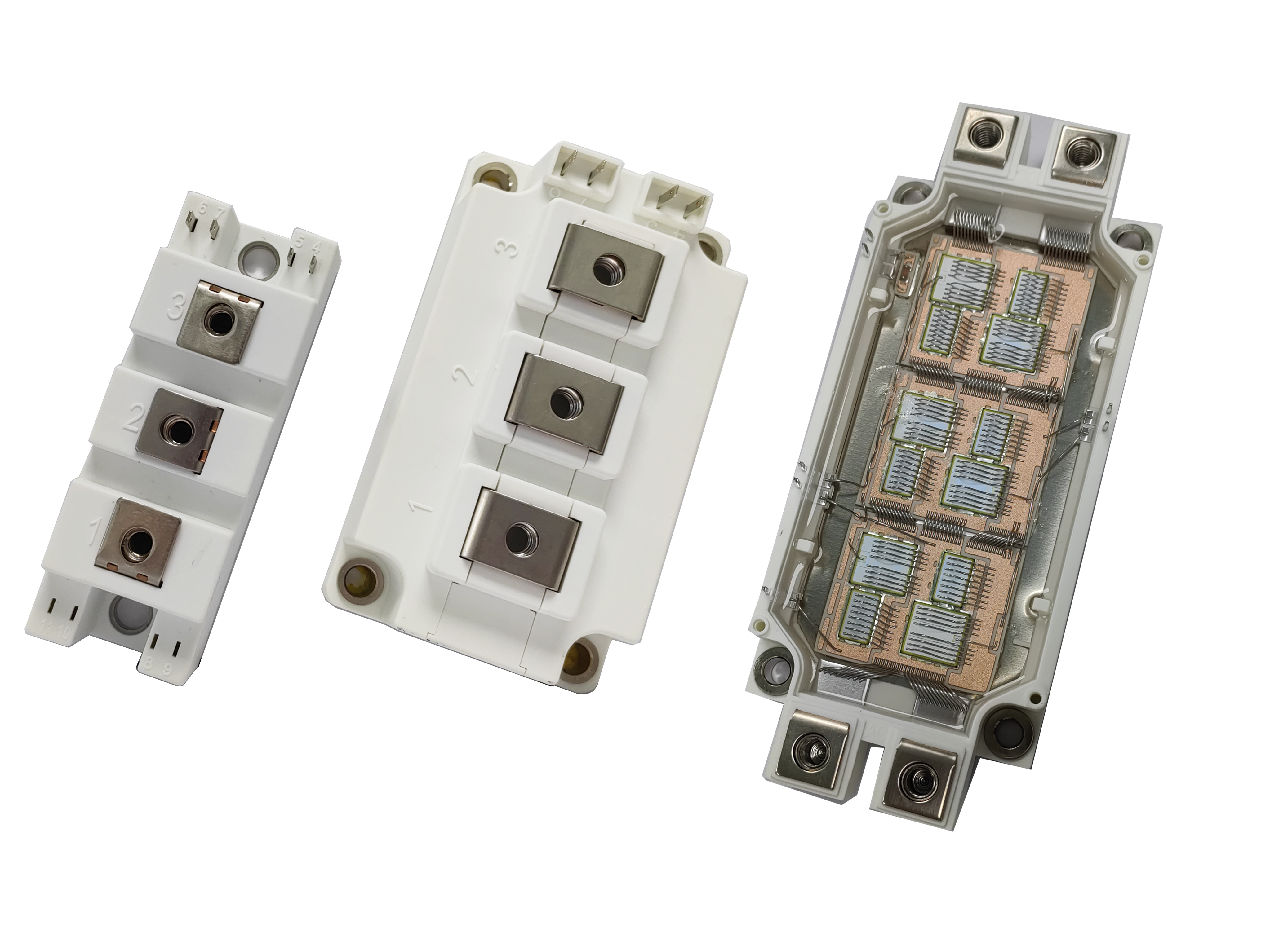
Reliable Power Control with 200A 400V Fast Recovery Diodes in Industrial Design
As industrial systems evolve toward higher power densities and faster switching speeds, the demand for durable, efficient diode components increases. Fast recovery diodes rated at 200A and 400V meet these expectations, especially when used in configurations tailored for automotive, welding, and inverter drive applications. This article focuses on how these diodes ensure reliability and thermal stability in industrial environments.
1. Stud-Type Diodes in Automotive Power Control
For applications where vibration resistance and mounting integrity are essential, the 3/4″-16UNF stud type automotive application high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode is the preferred solution.
It features a secure mechanical interface and excellent thermal transfer properties. Mounted directly to a vehicle chassis or heat sink, this diode maintains structural integrity under intense mechanical stress. In EV powertrains, it supports DC link filtering, boost stages, and battery management systems.
The 3/4″-16UNF stud type automotive application high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode also offers rapid recovery behavior that helps mitigate voltage transients caused by fast switching, improving overall system protection.
2. Efficient Power Conversion in Welding Systems
Industrial welders operate under dynamic current profiles and pulse frequencies. The common anode low conduction loss used in welding machine 200A 400V fast recovery diode is crafted to reduce internal resistance, making it ideal for these demanding conditions.
It lowers energy losses and enables quick response during load variations, essential for high-frequency pulsed MIG, TIG, or spot welding systems. The shared anode design also aids in thermal balancing and simplifies parallel diode configuration.
For OEMs building portable and high-duty-cycle welding machines, the common anode low conduction loss used in welding machine 200A 400V fast recovery diode delivers a compact footprint with scalable thermal performance.
3. Dual Diode Packages Streamline Inverter Performance
Space constraints and high-speed operation characterize modern inverter design. The dual diode for inverter drives high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode brings together two high-performance diodes in one housing, reducing component count and layout complexity.
This configuration supports VFDs, servo drives, and industrial UPS units by minimizing voltage overshoots and enhancing circuit responsiveness. Lower inductive paths and integrated thermal mass allow tighter EMI compliance and higher switching frequencies.
By adopting the dual diode for inverter drives high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode, designers simplify thermal design and maximize current handling in high-density layouts.
4. Layout Optimization for Longevity
Regardless of the diode type, layout and thermal considerations are key to maintaining system integrity:
Use torque-calibrated fastening and heatsinks for the 3/4″-16UNF stud type automotive application high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode.
Optimize copper trace width and spacing for the common anode low conduction loss used in welding machine 200A 400V fast recovery diode to prevent thermal bottlenecks.
Place the dual diode for inverter drives high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode near switching transistors to shorten current loops and reduce EMI.
Add TVS devices, active clamping, and proper snubber networks to protect all diode types from fault-induced transients and ensure high MTBF performance.
5. Conclusion
From automotive to industrial environments, the versatility and resilience of 200A 400V fast recovery diodes make them indispensable. The 3/4″-16UNF stud type automotive application high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode, common anode low conduction loss used in welding machine 200A 400V fast recovery diode, and dual diode for inverter drives high reliability 200A 400V fast recovery diode each serve distinct roles in enhancing system durability, efficiency, and performance across the industrial spectrum.