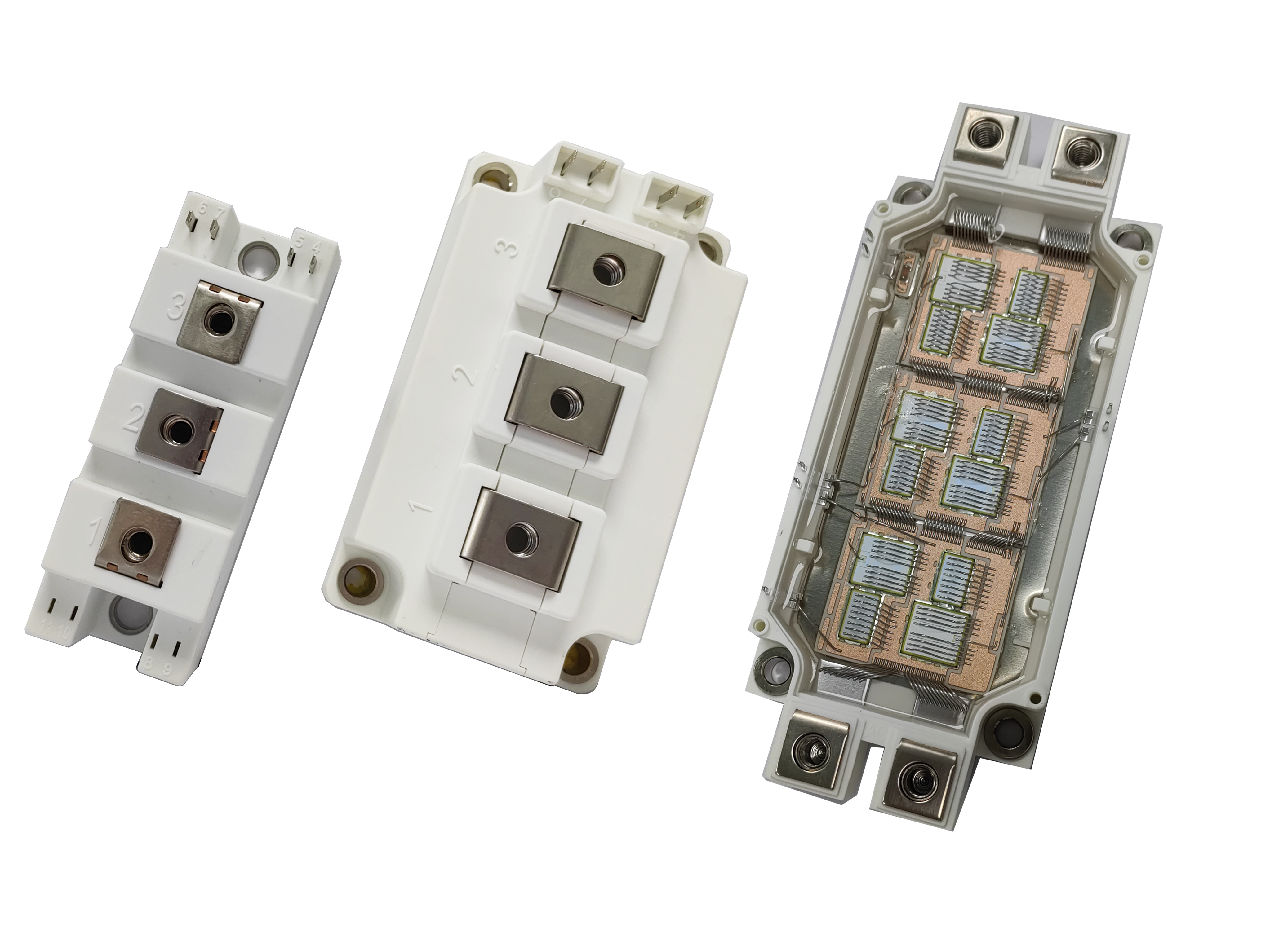
Diagnosing Common Issues in 600A Phase Control Thyristors for Industrial Applications
The 600A phase control thyristor is an essential power semiconductor device used in heavy industrial converters, rectifiers, and controlled AC drives. It is engineered for high thermal stability, high surge current rating, and high dv/dt immunity, allowing it to operate efficiently in environments with fluctuating electrical and thermal conditions. With its extended temperature range (–40°C to +85 °C) and low leakage current, this device is designed to provide consistent performance across a wide range of applications. However, even such robust components can experience failures due to thermal stress, improper gate triggering, or environmental contamination. Understanding how to troubleshoot these issues ensures reliability and extended service life.
A 600A phase control thyristor consists of a silicon PNPN structure encapsulated in a metal or disc-type housing for improved heat conduction. Its high thermal stability enables it to maintain performance even at elevated junction temperatures. Meanwhile, the high dv/dt immunity protects the device from false triggering during rapid voltage transitions.
The extended temperature range (–40°C to +85 °C) allows operation in demanding conditions, from subzero outdoor installations to high-temperature manufacturing environments. Low off-state leakage current ensures minimal power dissipation when the device is not conducting, maintaining system efficiency and reducing thermal load.
When properly implemented, these characteristics collectively support robust performance in rectifier bridges, welding systems, and variable speed drives.
Even with its advanced design, a 600A phase control thyristor can exhibit certain operational failures. The most common issues include unintentional triggering, increased leakage current, or open-circuit failure. To diagnose these faults effectively: Check gate trigger performance: Using an oscilloscope, verify that gate current pulses meet specifications and trigger uniformly across cycles. Inconsistent gate signals can cause incomplete turn-on, increasing losses and thermal stress. Measure leakage current: If leakage exceeds nominal values, inspect for contamination or moisture ingress. A low leakage current 600A phase control thyristor typically maintains microamp-level off-state currents under rated voltage. Evaluate dv/dt performance: In circuits with rapid voltage transients, ensure that high dv/dt immunity is not compromised by missing or faulty snubber components. Inspect for overheating: Excessive temperature rise above the extended temperature range (–40°C to +85 °C) can degrade junction characteristics and reduce the device’s high surge current rating.
Preventive maintenance is critical for sustaining long-term reliability. Engineers should focus on the following best practices: Maintain cooling efficiency: Ensure heat sinks and thermal interfaces are clean and properly clamped to preserve high thermal stability. Protect against voltage spikes: Install RC snubber networks to enhance high dv/dt immunity. Monitor temperature and load: Operate within the extended temperature range (–40°C to +85 °C) and avoid conditions that exceed the device’s rated high surge current rating. Periodic testing: Check for deviations in low leakage current to detect early signs of surface degradation. Environmental sealing: For outdoor or humid conditions, apply protective coatings to prevent leakage due to contamination.
A factory test revealed that neglecting cleaning and torque calibration led to rising leakage current in multiple 600A phase control thyristors, which was fully resolved after surface reconditioning and clamping correction.
The 600A phase control thyristor is built for demanding industrial use, featuring high thermal stability, high surge current rating, and high dv/dt immunity. Its extended temperature range (–40°C to +85 °C) and low leakage current design make it reliable under both extreme cold and heat. However, improper installation or lack of preventive maintenance can compromise performance. Regular inspection of gate control, cooling systems, and insulation integrity ensures optimal reliability. By following manufacturer datasheet specifications and proactive troubleshooting methods, engineers can extend the device’s operational lifespan and maintain consistent system performance.